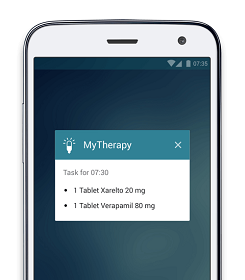
How an app can help reduce the risk of strokes via medication adherence, blood pressure monitoring, and lifestyle changes
You can reduce the risk of having a stroke via strict medication adherence to your anticoagulants and controlling your symptoms effectively. Find out how MyTherapy can help you below ...
A stroke happens when the blood supply to a part of your brain is either interrupted or reduced, meaning that the brain tissue is deprived of oxygen and nutrients. Brain cells begin to die very quickly and strokes therefore need to be treated as serious medical emergencies. Without quick and effective treatment, strokes can cause brain injury or death.
There are several long-term health conditions that can significantly increase the risk of developing strokes, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and atrial fibrillation. While medications specific to these conditions can alleviate their symptoms, these tablets often do not eliminate the risk of stroke. You will therefore need to take additional medication, such as anticoagulants (more commonly known as ‘blood thinners’). Anticoagulants essentially prevent your blood from clotting.
However, medications won’t work for you if you don’t take them correctly. Medication adherence can be challenging, especially with the hustle and bustle of day-to-day life. This is where medication and health tracker apps, like MyTherapy, can help you and offer you the support you need when it comes to medication adherence.
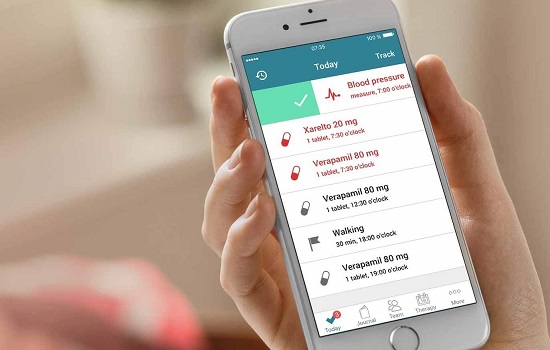
MyTherapy, one of Europe’s leading medication reminder and health tracker apps, was specifically developed for patients with long-term health conditions. The app generates personalized medication reminders each day, helping you take your medication exactly as prescribed by your healthcare professional. The medications can be added to the app by simply scanning the barcode of the packaging or by searching in the app’s built-in databases. You can also use the alarm notifications to remind you of any upcoming doctors’ appointments.
More than just a medication reminder, MyTherapy also features a digital health diary that you can use to log your blood pressure, cholesterol, weight, and other important measurements. You can also use the diary for tracking your health activities, such as walking or other forms of exercise.
All the data logged into the app is compiled into a monthly report, which you can share with your healthcare professional. This allows you to work closely with your doctor and ensures that you are doing well on your current treatment. The app, which is clinically proven to increase adherence rates, is also continuously being updated based on feedback from our users. This ensures that the team at smartpatient, the company behind the app, consistently works towards improving the app to meet your health needs.
The Main Symptoms of a Stroke
Strokes are often referred to as “brain attacks” and they can happen to anyone at any time. Strokes occur when the blood supply to part of the brain is reduced or cut off. They may be caused by a blocked artery (called an ischemic stroke) or the leaking/ bursting of a blood vessel (called a hemorrhagic stroke). When the blood supply is reduced or cut-off, the affected brain cells do not receive the oxygen and glucose they need to survive and begin to die. When these brain cells die, the abilities controlled by that specific area of the brain are lost (for example, memory and muscle control). Strokes can lead to brain injury, disability, and death; so the earlier they are treated, the less the damage will be. Because different parts of the brain affect different parts of the body, the symptoms of a stroke depend on which area of the brain is affected. For this reason, the signs of a stroke vary from person to person. In most cases, the onset of symptoms is sudden and typically affect the face, speech, and arm strength due to paralysis or numbness. For example, a person experiencing a stroke may be unable to smile and lift both arms and keep them up and his/ her speech may be slurred and unclear.
Aside from these main symptoms, several others exist:
- Paralysis of one side of the body
- Trouble with seeing in one or both eyes
- Sudden confusion, dizziness, or unsteadiness
- Sudden severe headaches
- Problems understanding other people
- Difficulties swallowing
- Loss of consciousness
If you suspect that you are or someone else is having a stroke, you must call an ambulance immediately. The quicker a stroke is treated, the less brain damage there will be.
In a related condition called a transient ischemic attack (TIA), the blood supply to the brain is only interrupted temporarily. Therefore, TIAs are often referred to as “mini-strokes”. They cause the same symptoms of a stroke, but only last for a short period of time and not longer than 24 hours. TIAs can be used as a warning sign that a full stroke can occur. Once again, you should call emergency services immediately if you experience stroke-like symptoms.
Ischemic Strokes and Hemorrhagic Strokes
There are two types of strokes that each have different causes.
In ischemic strokes, the arteries to your brain become narrowed or blocked. The most common types of ischemic strokes include thrombotic strokes and embolic strokes. Thrombotic strokes happen when a blood clot forms in one of the arteries that supplies blood to your brain. In embolic strokes, a blood clot forms somewhere else in the body and then travels through your blood stream where it lodges in one of the narrower brain arteries. Ischemic strokes account for 85% of all strokes and, apart from age, there are several factors that can increase the risk of ischemic strokes. These include:
- Smoking
- Having high blood pressure (hypertension)
- Being overweight or obese
- Having high levels of cholesterol
- Having diabetes
- Drinking an excessive amount of alcohol
Moreover, having atrial fibrillation (AFib) also significantly increases the risk of stroke. AF causes an irregular and accelerated heartbeat. It can lead to the formation of blood clots in the heart, which can become dislodged and travel into the blood vessels of the brain. Read more about AFib here.
Hemorrhagic strokes occur when a weakened blood vessel supplying the brain ruptures. This causes bleeding in or around the brain tissue. Hemorrhagic strokes are often caused by high blood pressure. Factors that increase blood pressure include being overweight or obese, excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, inactivity, and stress. Hemorrhagic strokes may also be caused by a brain aneurysm, which is a balloon-like expansion of a blood vessel in the brain. Aneurysms have very thin blood vessel walls that can rupture easily.
In England, approximately 110,000 people have a stroke each year. In the United States, this number is as high as 800,000. This makes stroke the third largest cause of death (after heart disease and cancer), as well as a major cause of disability in adults.
Treatment Options and Prevention
The treatment of strokes depends on what type of stroke you have had (ischemic stroke or hemorrhagic stroke), which area of the brain is affected, and what caused the stroke. Often, strokes are treated with medication to prevent blood clots and reduce blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Sometimes surgery will be necessary to reduce brain swelling or repair damaged blood vessels.
The best way to prevent strokes is to follow a healthy lifestyle. This means eating a balanced and healthy diet, exercising regularly, drinking alcohol in moderate amounts, and not smoking. People who are diagnosed with a health condition that increases the risk of stroke may require medication. Conditions which can increase the risk of having a stroke include:
- High cholesterol
- High blood pressure
- Atrial fibrillation
- Diabetes
- TIAs
For each condition there is a special type of medication and treatment plan that can help reduce the risk of stroke. For instance, high cholesterol can be treated with statins, aspirin, or ezetimibe. Medications for high blood pressure may include ACE inhibitors or beta-blockers. However, for many conditions that increase the risk of strokes, especially atrial fibrillation, anticoagulants are prescribed. These medicines do not alleviate the original condition (e.g. AFib), but help prevent the formation of blood clots by changing the chemical composition of the blood. The most common anticoagulant that is prescribed is warfarin. The efficacy of warfarin depends on the correct dosage in your system and can easily be affected by your diet. Therefore, warfarin requires constant monitoring and blood tests. There is also a new class of medicines available: the so-called novel oral anticoagulants (NOACs). They include apixaban (Eliquis), dabigatran (Pradaxa), and rivaroxaban (Xarelto). These are just as effective as warfarin, but are easier to manage. For example, they require less monitoring and blood tests and have less food interactions. Anticoagulants can cause various side effects. Therefore, it is necessary to discuss the treatment plan with your doctor before taking any medication.
Use MyTherapy and Lower Your Risk Today
Several long-term health conditions increase the risk of a stroke and managing these health conditions is essential to lowering this risk. If you are at risk, you should use MyTherapy to help you make important lifestyle adjustments and manage your medication. With its reliable medication reminders, the app helps you to take your medication on-time, each day. This helps you get into a routine and ensures that you achieve maximum efficacy and fewer side-effects from your medication. The app’s digital health journal will also encourage you to track your blood pressure, cholesterol levels, weight, and side-effects, ensuring that you monitor your health carefully and consistently. You can also use the app to record any lab values. All this information can be used by your doctor to see how you are doing and adjust your treatment plan if needs be. These features, in combination with the user-friendly design, make the app a valuable companion in managing long-term health conditions and reducing the risk of stroke.